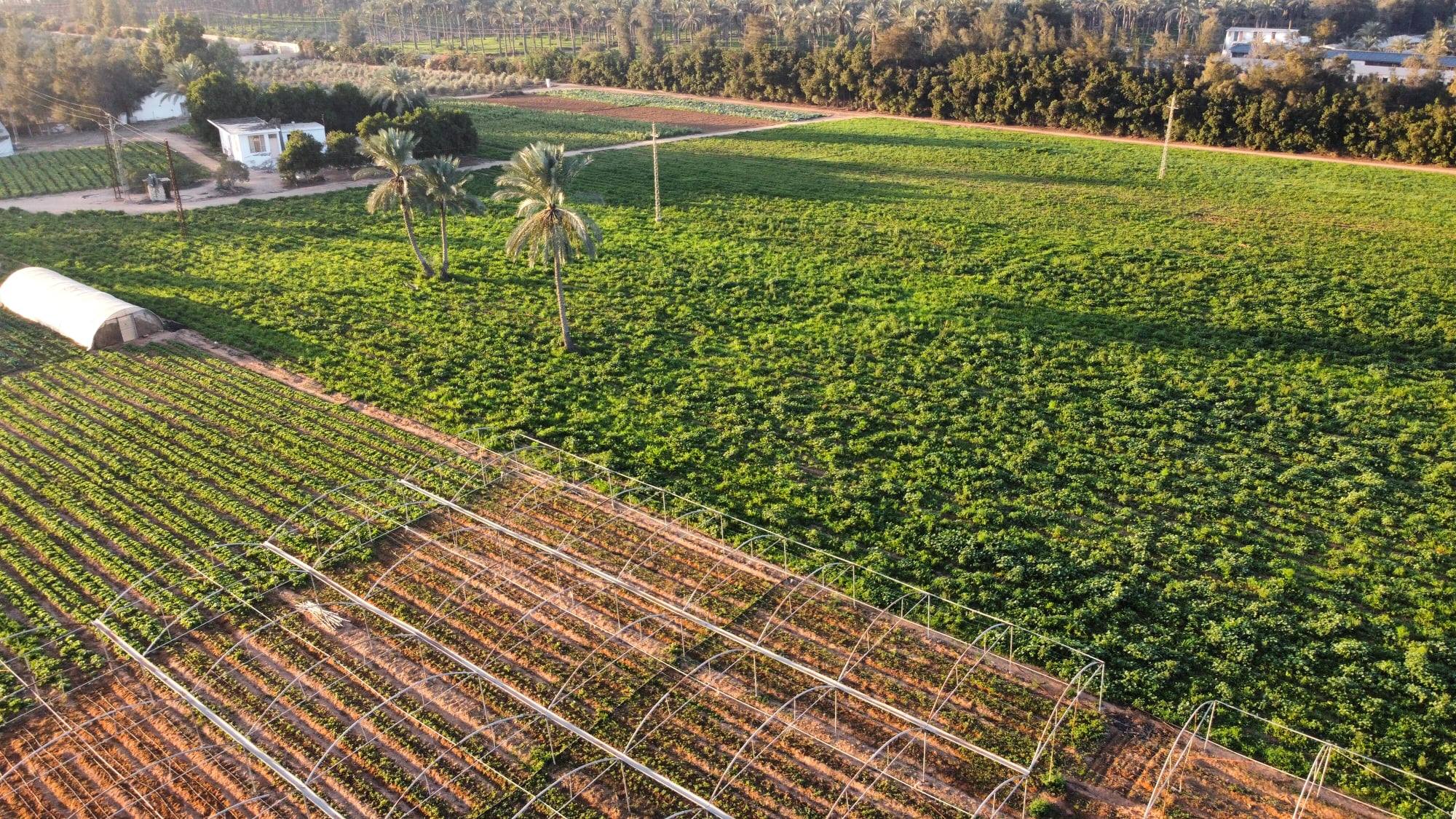
Organic and Biodynamic agriculture are systems that aim to make the best use of environmental goods and services without damaging the natural, social and human capitals, thus rendering them inherently sustainable. These agricultural models are holistic production management systems whose primary goal is to optimize the health and productivity of interdependent communities of soil, life, plants, animals and people. They rely on an ecosystem approach based on sustainable ecosystems, safe food, good nutrition, animal welfare and social justice, they follow the principles of logic of a living organism and aim to produce food while sustaining the health of soils, ecosystems and peoples, by combining tradition, innovation and science to benefit the shared environment and promote fair relationships and good quality of life for all involved. Both organic and biodynamic agriculture rely biodiversity and ecological process such as crop rotation, intercropping, integrated pest management, and compost, they prohibit the use of chemical fertilizers, herbicides and pesticides, genetically modified organisms, growth regulators, feed additives and hormones, to ensure an optimal level of production without compromising the conditions of farmers, lands and the environment. Unlike the conventional model, the organic and biodynamic counterparts represent a deliberate attempt to make the best use of local natural resources and aim to create integrated, humane, environmentally and economically viable agricultural systems.
Following these principles, organic and biodynamic agriculture aim to: Work as much as possible within a closed system, and draw on local resources; maintain the long-term fertility and soils; avoid all forms of pollution that may results from agricultural techniques; provide products of high nutritional quality and sufficient quantity; reduce the use of fossil energy to a minimum; Give livestock conditions of life that conform to their physiological needs and to humanitarian principles; and Make it possible for agricultural producers to earn a living through their work and develop their potential as human beings.